CS5229 Advanced Computer Network 课程笔记。
目录:
- L0 Prerequisite
- L1 Internet Architecture
- L2 SDN/NV
- L3 Queueing Theory
- L4 Traffic Models
- L5.1 Scheduling & Fairness
- L5.2 Buffer Management
- L6 Congestion
- L7 Topology & Load Balance
Prerequisite
Internet Architecture
You know what the following terms mean: router, switches, ISP, AS.
- router: Machine which forwards the packet from the source to the destination. Routers are usually used in the network core.
- switches: Machine which forwards the packet from the source to the destination. Switches (specifically, link-layer switches) are usually used in access networks.
- ISP: Internet Service Provider. ISP is something that provides the customers with internet access, where the word “customers” means not only the clients but also the content providers (e.g. websites and video).
- My question (a): Why does ISP exist? See the answer below.
- AS: Autonomous System. A set of routers under a single technical administration.
- My question (b): Why does AS exist? question (c): what’s the difference between ISP and AS? See the answer below.
You know how Internet is different from a Telephony network.
- Telephone network is a circuit-switched network while Internet is a packet-switched network.
- My question (d): What is circuit-switched network? See the answer below.
- Telephone network is a circuit-switched network while Internet is a packet-switched network.
You frown when someone equates the Internet with the Web.
- Web is the content which will be transmitted via Internet. It is stored in end system (servers) and accessed by the users. Internet, however, is a network. We can understand Internet in two perspectives: (i) The complex made up of hardwares and softwares, and (ii) Networking infrastructure that provides services for distributed applications.
- Answer to question (a): Building connections between hosts are very expensive and complicated which is unacceptable to individuals. Therefore, we need big organization to build the connection systems and provide access service for individuals, which is much cheaper because (i) one system for all the customers, it spreads the cost over hundreds and thousands of customers, and (ii) scientific management over a big system can save a lot of money.
- Answer to question (b): (i) Scale. As the number of routers becomes large, it is impractical to transit and store all the routing algorithms. (ii) Administrative autonomy. ISPs may want to manage routers in different ways (e.g. use different routing algorithms).
- Answer to question (c): ISPs are business organisations, while AS is a technical structure. Different ISPs can share the same AS, one ISP can partition their routers into different ASs. See reference.
- Answer to question (c): In circuit-switched network, the sender and receiver need first build a real connection and then transmit message. The messages are transmitted in a constant transmission rate. On the contrary, in packet-switched network, sender and receiver don’t need to build a real connection and the messages are not transmitted in a certain transmission rate.
Naming/Addressing
You know what is a domain name, what is an IP address, and how to map between the two.
- Domain name: name to identify the host. It’s more like a nickname, easy to use and remember.
- IP address: name to identify the host. It consists of four bytes, looks like 121.7.106.83. It’s hard for human to use but easy for the router to process.
You know how DHCP assigns a dynamic IP address to you host.
- DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. The DHCP allows the network admin to allocate the IP address to the host automatically. The IP address can be constant/permanent for the host, it can also be different every time the host connects to the network.
- The way DHCP works can be concluded in 4 steps :
- DHCP server discovery. The client will send a broadcast to all the node in the subnet to find the DHCP sever(s).
- DHCP server offer(s). The DHCP server who receives the DHCP discover message will broadcast a response with proposed IP address.
- DHCP request. The client receiving the offer message(s) will choose one offer and response to the selected server with a DHCP request message.
- DHCP ACK. The server will response the client with a DHCP ACK message.
Protocol Layers
- You know the functionalities of 5 layers of the Internet protocol stack.
- Application Layer: The application layer is where network applications and their application-layer protocols reside such as HTTP, SMTP and FTP.
- Transport Layer: The Internet’s transport layer transports application-layer messages between application endpoints. In the Internet there are two transport protocols, TCP and UDP, either of which can transport application- layer messages.
- Network Layer: The Internet’s network layer is responsible for moving network-layer packets known as datagrams from one host to another. There are two kind of important protocols: IP protocol and routing protocol.
- Link Layer: The Internet’s network layer routes a datagram through a series of routers between the source and destination. To move a packet from one node (host or router) to the next node in the route, the network layer relies on the services of the link layer.
- Physical Layer: While the job of the link layer is to move entire frames from one network element to an adjacent network element, the job of the physical layer is to move the individual bits within the frame from one node to the next.
Application Protocol
- You roughly know how HTTP and FTP works.
- HTTP
- FTP
Transport Protocol
You know what is a port and socket.
You can tell the differences between TCP and UDP. You know in what situation you should use which.
TCP
- You know why congestion control and flow control are needed. You roughly know how TCP’s congestion control works.
Network Layer
You know that almost everything runs on IP. You know how packets are routed on the Internet, at least within an AS.
You know what’s a private IP address and why NAT makes P2P file sharing difficult.
Ethernet
You know why Ethernet is a random access protocol. You know what collision and backoff mean in this context.
When people talked about “MAC address” you didn’t think it’s related to location of nearest McDonald.
You know how mapping between MAC and IP addresses is done.
Tools
- You have used ping or traceroute. Or at least heard about them and know what they are for.
Basic Probability
You know what is expected value, variance, random variable, and cumulative distribution function.
You know how to compute conditional probability and probability of two events.
Programming
- You know how to program in C or C++, and is comfortable in picking up new languages.
L1 Internet Architecture
pass.
L2 SDN/NV
2 topics
- Network Programmability (SDN)
- Network Virtualisation (NV)
Network Programmability
Why SDN
- Advantages of SDN
- Disadvantages of traditional network
- routers/switches
- control plane
- data plane
- Separation of control and data plane
Before 2008:
- Active Network
2008-09: SDN Era (OpenFlow)
- Features
- In Control Plane perspective
- How does it work
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Architecture
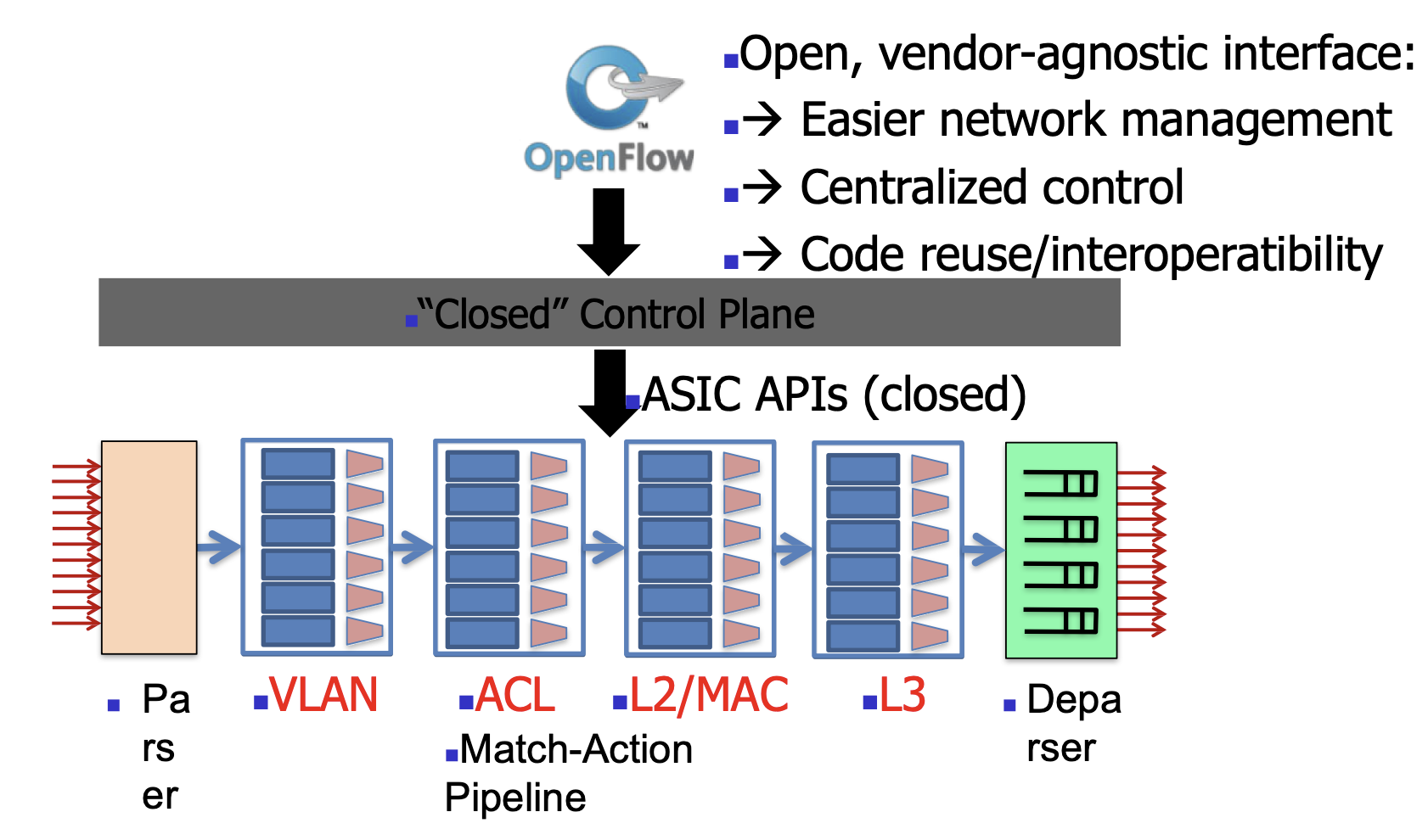
2013-14: Programmable Switches
- Features
- In Data Plane perspective
- How does it work
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Architecture
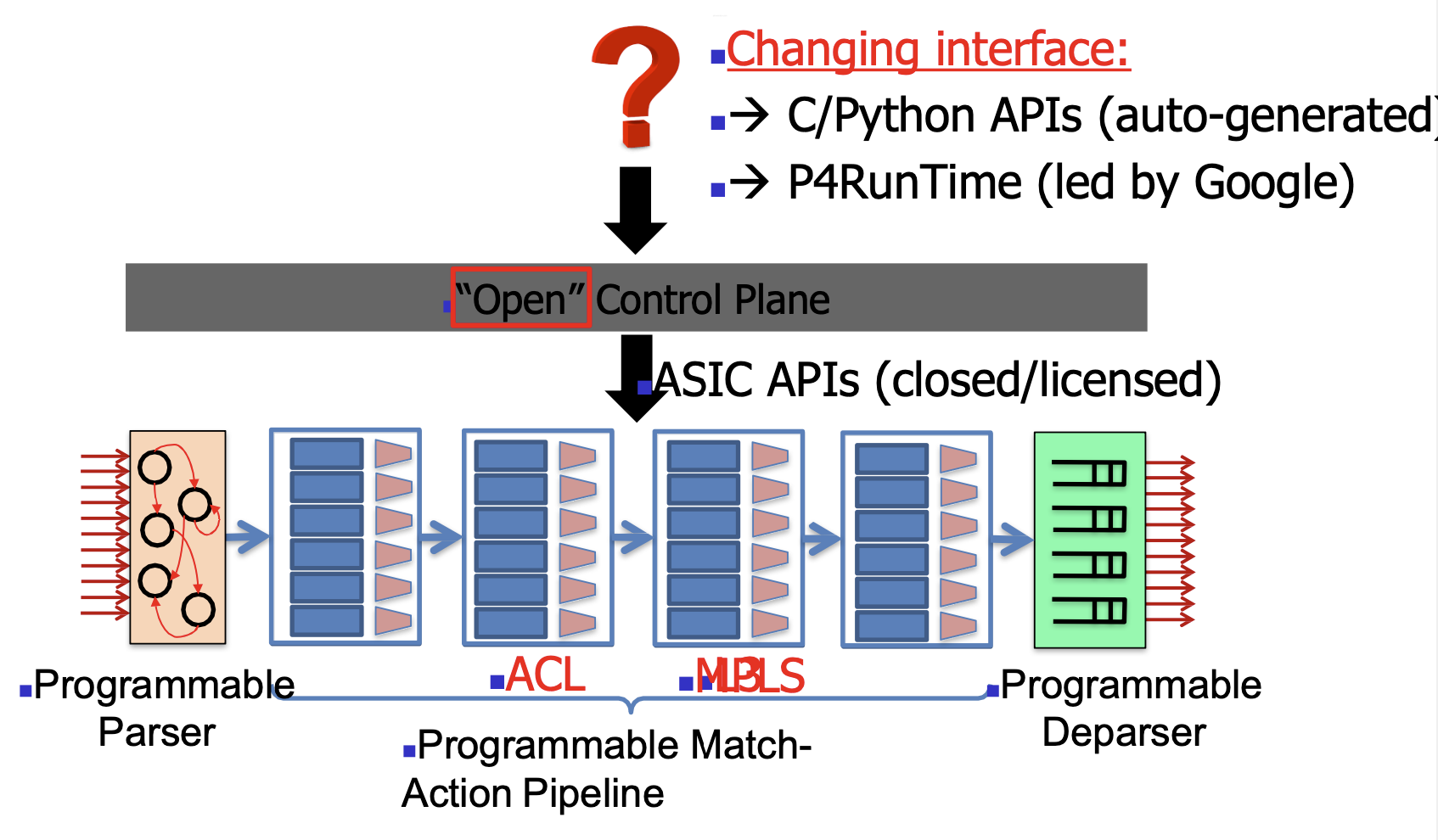
Network Virtualisation
- What is NV
- Why NV
- Components of NV
- Cases
- virtual switches
- flow space slicing
- Compare NV with SDN
- SDN alone does not abstract away details of physical network
- SDN is not required for NV, but SDN makes NV much easier
- NV is also a way to enable abstractions
Virtualisation in Data Center
- Why
- Achieve high utilisation to be cost effective
- Main objective
- Uniform high capacity from server-to-server
- Performance isolation
- Layer-2 semantics
- How
- Multiple Routing
- VLB
- ECMP
- Addressing and Routing
- Multiple Routing
L3 Queueing Theory
Important concepts:
- Birth-Death Process
- State Transition Diagram
- M/M/1
- M/M/m
- M/M/1/K
- M/M/m/m
- Different Scenario
- Written Assignment
L4 Traffic Models
Internet Traffic, Web Traffic
- Distribution of Traffics
- Lognormal, Weibull, Gamma
- Q-Q Plot
- Heavy Tail
- Pareto Distribution
- Conditional Mean Exceedance (CME)
Data Center Traffic
- Traffic Shaping: shape the traffic to reduce any adverse impact on the network
- leaky/token bucket: limit input to specified Burst Size and Average Rate.
L5 Scheduling&Fairness
Outline
- **What is scheduling, why we need it?
- **Requirements of a scheduling discipline
- **Fundamental choices
- **Scheduling disciplines
- **Buffer management and packet drop strategies
A scheduling discipline does two things
- decides service order (scheduling)
- manages queue of service requests (buffer management)
Requirements for scheduling disciplines
- easy to implement
- fair: share resources fairly
- provides performance bounds: provide some form of performance guarantees
- allows easy admission control decisions
Scheduling disciplines
- service-time dependant scheduling
- first-in-first-out, FIFO
- Cons: cannot differentiate between packets
- Pros: easy
- shortest processing time first, SPT
- shortest remaining processing time first, SRF
- first-in-first-out, FIFO
- However, service-time dependent scheduling are not common in packet switching because the packet ordering will be modified and delay for large packets increases
- service-time dependant scheduling
Fairness: How to measure the fairness of scheduling?
- Jain’s index: equal resource share as the objective
- Max-min fairness: water filling
- General Process Sharing, GPS
- Distribute the recourse equality to all the connections
- Impossible to implement but Can be a baseline.
- Weighted Round Robin (emulate GPS because we cannot implement GPS)
- Problem: (i) With variable size packets and different weights, need to know mean packet size in advance. (ii) Can be unfair for long periods of time.
- Weighted Fair Queueing, WFQ (Deals better with variable size packets and weights)
- *Variant of FQ: WF^2Q (A packet can arrive later and yet be served earlier)
- General Process Sharing, GPS
L5 Buffer Management
- Buffer Management
- Packets that cannot be served immediately are buffered
- How should the buffer be shared among flows/connections?
- When buffers is full, a packet drop strategy is needed
- Packet losses happen almost always from best-effort connections (why?)
- Typically, packets are dropped only when buffer is full (why?)
- Drop Strategies
- Degree of aggregation
- Drop priorities
- Drop lower-priority packets first
- Drop position
- head, tail, random, drop entire longest queue
- When to drop?
- Early Drop: drop arriving packet with fixed drop probability if queue length exceeds threshold
- Random Early Detection (RED)
- Late Drop
- Early Drop: drop arriving packet with fixed drop probability if queue length exceeds threshold
- Buffering Sharing
- Q: if it is possible to provide separate queues for different traffic flows/classes, how much buffer space should be allocated to each flow/class?
- Static
- Dynamic
L6 Congestion
- Motivation
- Sender should adjust the send speed according to the receiver and network (feedback from receiver and network).
- Hard to achieve: (i) delay between sender and receiver, (ii) state change.
- Questions
- How to measure the feedback?
- How to determine whether to send more/less data?
- How to determine whether to send fast/slowly?
- Model from A Binary Feedback Scheme for Congestion Avoidance in Computer Networks with a Connectionless Network Layer
- Window-based Control
- Policy on router and user
- Router
- Feedback
- congestion bit (1: congested, 0: not congested)
- Congestion Detection
- Detect congestion when the average number of packets at the router is greater or equal to 1. According to Queueing Theory, M/M/1, $N=\rho/(1-\rho)$.
- Feedback
- User
- Decision on window size
- Linear Control
- $$ \begin{aligned} &x_i(t+1) \ &\quad= \begin{cases}a_1+b_1 x_i(t) & \text { if } y(t)=0 \Rightarrow \text { Increase } \ a_{\mathrm{D}}+b_{\mathrm{D}} x_i(t) & \text { if } y(t)=1 \Rightarrow \text { Decrease }\end{cases}\end{aligned} $$
- Four options to determine the Linear Control parameter, (slide 19)
- Criteria for Selection $\uparrow$ (slide 20)
- Main Result (slide 30): According to fairness, optimal option is (Additive Increase, Multiplicative Decrease.)
- Max-Min Flow Control
- Proportional Fair
- Linear Control
- Decision on window size
- Router
- TCP Reno
- AIMD (Additive Increase, Multiplicative Decrease) Model
- Too low
- AIMD (Additive Increase, Multiplicative Decrease) Model
- TCP Cubic: the current default TCP algorithm used by the Linux kernel
- Quickly increase from Wmin and slow down before Wmax to probe for the “right” network condition
- TCO Vegas
L7 Topology&Load Balance
- Topology Questions
- How to connect all the devices in data center?
- What need to achieve?
- Scalable interconnection bandwidth (high bisection bandwidth)
- Low Cost
- Compatible with existing system (use of TCP/IP and Ethernet)
- Fat-Tree
- K pods, each containing two layers of k/2 switches
- Each k-port switch in the lower layer is connected to k/2 hosts and k/2 switches in the upper layer
- Each k-port switch in the upper layer is connected to k/2 core switches
- Routing Question
- Many possible shortest paths, want to “spread load” over different paths
- Need for multiple path forwarding for different flows with the same source-destination addresses
- Dynamic Routing
- Flow Classification
- Flow Scheduling
- 本文作者: YA
- 本文链接: https://shiyuang-scu.github.io/2022/12/17/【学习笔记】CS5229-Advanced-Computer-Network/
- 版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 MIT 许可协议。转载请注明出处!


